The way we save and access data has been transformed by how does cloud storage work, which offers a practical and adaptable approach to manage files and data. However, have you ever wondered how does cloud storage work functions in practice? We will examine the underlying ideas of cloud storage and shed light on the mechanisms underlying this ground-breaking technology in this introduction.
Cloud storage is fundamentally a way to store data on distant servers that can be accessed online. Cloud storage uses a network of servers maintained by how does cloud storage work, as opposed to local storage devices like hard drives or physical servers. These servers are often kept in data centers with cutting-edge equipment and strong security procedures. newlifedn.com will provide some of information for you in this post.
Contents
What is Cloud Storage?

Digital data is saved on servers located off-site in a kind of computer data storage known as how does cloud storage work. A third-party supplier who is in charge of hosting, administering, and protecting the data kept on its infrastructure maintains the servers. The service provider guarantees that data stored on its servers is always reachable across open or secure internet connections.
Organizations can store, access, and maintain data using how does cloud storage work, eliminating the need for them to own and run their own data centers and shifting costs from a capital investment model to an operating one. Because cloud storage is scalable, businesses can change the size of their data footprint as needed.
How does Cloud Storage work?
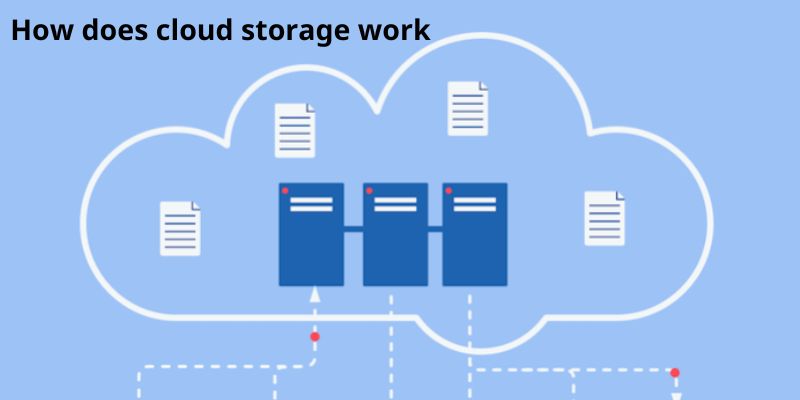
To store data, including files, business data, videos, or photographs, how does cloud storage work uses remote servers. Users use an internet connection to upload data to servers, where it is stored on a virtual machine on a physical server. Cloud service companies frequently distribute data over numerous virtual machines in different data centers around the world to maintain availability and provide redundancy. The cloud provider will start up more virtual computers to manage the load if storage requirements rise. Through an application programming interface (API) and software such as a web portal, browser, or mobile app, users can access data in cloud storage.
Four models of how does cloud storage work are available:
Public
According to the public cloud storage concept, a company stores its data in a service provider’s data centers, which are also used by other businesses. Public Cloud Storage offers data on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis and disperses it over several geographical areas. The term “elastic” refers to the ability of public cloud storage to scale up or down in response to organizational needs. Data is often accessible from any device, including a smartphone or online portal, thanks to how does cloud storage work.
Private
A company using its own servers and data centers to store data inside its own network is referred to as using how does cloud storage work. As an alternative, businesses can work with cloud service providers to have exclusive access to dedicated servers and private connections. Organizations that need more control over their data and have strict compliance and security needs are more likely to choose private clouds.
Hybrid
A hybrid cloud storage solution combines private and how does cloud storage work. Organizations have the option to select whatever data they wish to store in which cloud using a hybrid cloud storage architecture. While less sensitive data is stored in the public cloud, sensitive data and data that must adhere to high compliance standards may be kept in a private cloud. A layer of orchestration is often present in a hybrid cloud storage strategy to facilitate integration between the two clouds. Organizations can still scale up with the public cloud using a hybrid cloud, providing flexibility.
Multicloud
When a company sets up many cloud models from various how does cloud storage work (public or private), they are using a multicloud storage model. If one cloud vendor offers specific proprietary apps, if the organization needs data to be stored in a specific country, if different teams are trained on different clouds, or if the organization needs to meet different requirements that are not covered by the service providers’ SLAs, then the organization may opt for a multicloud model. Organizations can benefit from flexibility and redundancy with a multicloud approach.
Advantages of Cloud Storage

Total cost of ownership
With the help of cloud storage, businesses may swiftly switch from a capital expenditure strategy to an operating expense model.
Elasticity
According to the requirements of the company, cloud storage can be scaled up (more storage can be added) or down (less storage is required).
Flexibility
Cloud storage gives businesses freedom in how they deploy and allocate resources, store and access data, and design their IT infrastructure.
Security
The majority of cloud service providers provide strong security, including cutting-edge software and application security as well as physical protection at data center levels. Zero trust architecture, identity and access management, and encryption are all provided by the top cloud service providers.
Sustainability
The overhead of energy usage is one of the biggest expenses when running data centers on-site. The leading cloud service providers use renewable energy sources to run their operations.
Redundancy
Public clouds include built-in redundancy (the replication of data across several servers in various locations), which enables businesses to recover from calamities while maintaining business continuity.
Disadvantages of Cloud Storage
Compliance
Data storage and access are strictly regulated in some sectors, including finance and healthcare. Some public cloud service providers give resources to help users stay compliant with any relevant laws and regulations.
Latency
Due to network traffic congestion or sluggish internet connections, traffic to and from the cloud may be delayed.
Control
In exchange for trusting that the cloud service provider will always be able to keep that data available and maintain its systems and security, storing data in public clouds results in a loss of some control over access and management of that data.
Outages
Although public cloud services strive to guarantee constant availability, outages occasionally do happen and render stored data unusable.






